Food That Help Lower Cortisol
Stress has become an almost inevitable part of life. Whether it’s work deadlines, personal responsibilities, or the constant buzz of technology, our bodies are often in a state of heightened alertness. This stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Chronically elevated levels can lead to a host of health issues.
About Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands, which are small glands located on top of the kidneys. Often referred to as the “stress hormone,” cortisol plays a crucial role in several bodily functions, particularly in how the body responds to stress. Here’s a breakdown of what cortisol does and why it’s important:
Key Functions of Cortisol
Stress Response:
Cortisol is released in response to stress, whether physical (like illness or injury) or psychological (like work pressure or anxiety). It helps the body mobilize energy and resources to deal with the stressor, often referred to as the “fight-or-flight” response.
Metabolism Regulation:
Cortisol helps regulate metabolism by influencing how the body processes carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It ensures that the body has enough energy by increasing blood sugar levels through gluconeogenesis (the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources).
Immune System Modulation:
Cortisol has anti-inflammatory properties and helps regulate the immune system. While this can be beneficial in the short term, chronic high levels of cortisol can suppress immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Blood Pressure Regulation:
Cortisol helps maintain blood pressure by enhancing the action of adrenaline and constricting blood vessels. This ensures that oxygen and nutrients are delivered efficiently to tissues during stressful situations.
Sleep-Wake Cycle:
Cortisol follows a diurnal rhythm, meaning its levels fluctuate throughout the day. It’s typically highest in the morning (to help you wake up and feel alert) and gradually decreases throughout the day, reaching its lowest point at night to promote restful sleep.
What Happens When Cortisol Levels Are Too High or Too Low?
High Cortisol Levels (Hypercortisolism):
Chronically elevated cortisol levels, often caused by prolonged stress, can lead to a range of health issues, including:
Weight gain (especially around the abdomen)
High blood pressure
Weakened immune function
Sleep disturbances
Mood disorders (like anxiety and depression)
Increased risk of chronic diseases (like diabetes and heart disease)
Low Cortisol Levels (Hypocortisolism):
Insufficient cortisol production, as seen in conditions like Addison’s disease, can cause symptoms such as:
Fatigue
Low blood pressure
Weight loss
Muscle weakness
Mood swings
Foods to Eat to Manage Cortisol Levels
What you eat can play a significant role in managing cortisol levels. By incorporating certain foods into your diet, you can help your body better cope with stress and promote a sense of calm. Here’s a list of cortisol-lowering foods to add to your plate:
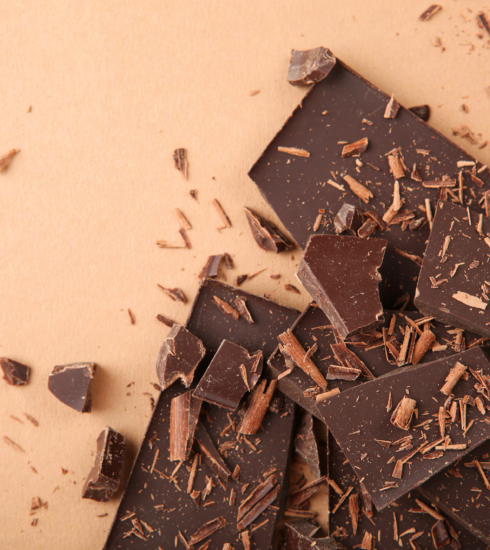
1. Dark Chocolate (Yes, Really!)
Dark chocolate (with at least 70% cocoa content) is rich in antioxidants and flavonoids, which have been shown to reduce cortisol levels. It also contains magnesium, a mineral known to promote relaxation. Enjoy a square or two as a guilt-free treat to help soothe your nerves.
2. Fatty Fish
Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and other fatty fish are packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and can help regulate cortisol production. Studies suggest that omega-3s can also improve mood and reduce stress. Aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week.
3. Leafy Greens
Spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and other leafy greens are high in magnesium, a mineral that plays a key role in managing cortisol levels. Magnesium helps relax the nervous system and can counteract the effects of stress. Add a handful of greens to your smoothies, salads, or stir-fries for a calming boost.
4. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are excellent sources of healthy fats, magnesium, and zinc, all of which help regulate cortisol. They also provide a steady release of energy, preventing blood sugar spikes that can exacerbate stress. Keep a small handful of nuts or seeds on hand for a quick, stress-busting snack.
5. Oats
Oats are a complex carbohydrate that helps stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing cortisol spikes. They also contain tryptophan, an amino acid that promotes the production of serotonin, a feel-good neurotransmitter. Start your day with a warm bowl of oatmeal topped with berries and nuts for a calming breakfast.
6. Berries
Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, which help combat the oxidative stress caused by high cortisol levels. Their natural sweetness can also satisfy sugar cravings without causing a blood sugar crash.
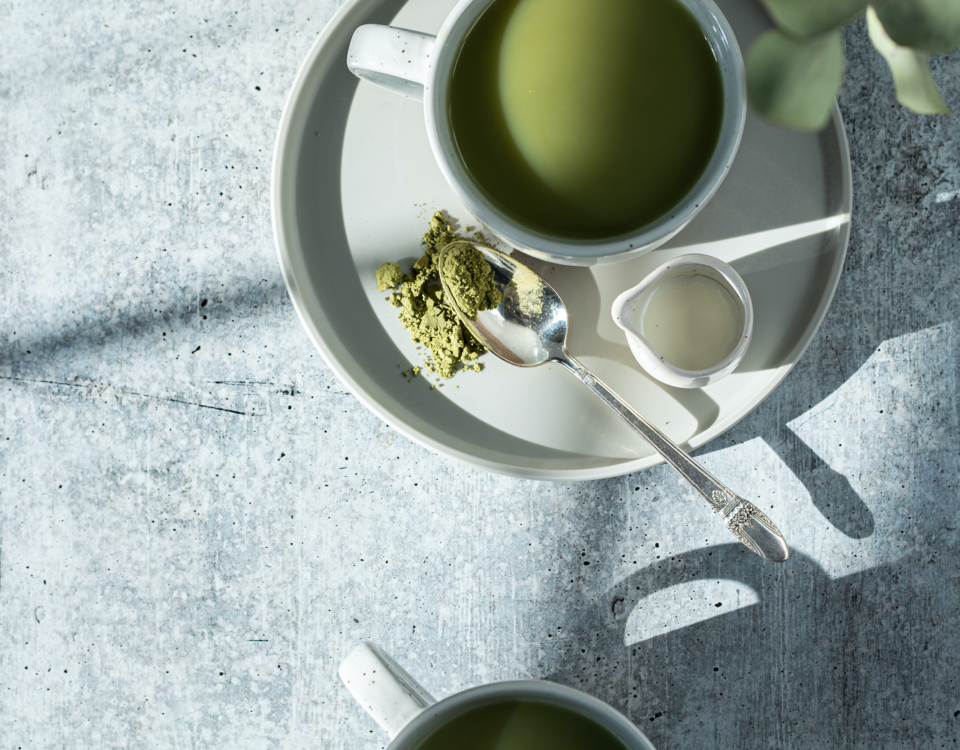
7. Green Tea
Green tea contains L-theanine, an amino acid that promotes relaxation without causing drowsiness. It also helps lower cortisol levels and improve focus. Swap your afternoon coffee for a cup of green tea to reduce stress and stay alert.
8. Avocados
Avocados are a great source of healthy fats, potassium, and B vitamins, all of which support adrenal health and help regulate cortisol. Their creamy texture and versatility make them a delicious addition to salads, toast, or smoothies.
9. Fermented Foods
Gut health and stress are closely linked, and fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are rich in probiotics that support a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut can help reduce cortisol levels and improve overall mood.
10. Bananas
Bananas are rich in potassium, which helps regulate blood pressure—a common issue during times of stress. They also contain tryptophan, which supports serotonin production, and vitamin B6, which helps the body process stress hormones more effectively.
11. Turmeric
This vibrant yellow spice contains curcumin, a compound with powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Curcumin has been shown to reduce cortisol levels and protect the body from the damaging effects of chronic stress. Add turmeric to soups, curries, or golden milk for a soothing effect.
12. Chamomile Tea
While not a food, chamomile tea deserves a mention for its calming properties. It has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for stress and anxiety. Sipping on a warm cup of chamomile tea before bed can help lower cortisol levels and promote restful sleep.
13. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are a nutrient-dense carbohydrate that helps stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing cortisol spikes. They’re also rich in beta-carotene, which supports immune function and reduces inflammation.
14. Eggs
Eggs are a great source of high-quality protein and contain essential nutrients like choline, which supports brain health and helps regulate stress responses. Start your day with a protein-rich breakfast to keep cortisol levels in check.
15. Garlic
Garlic contains sulfur compounds that boost glutathione production, an antioxidant that helps combat oxidative stress caused by high cortisol levels. Add fresh garlic to your meals for both flavor and stress relief.
16. Asparagus
Asparagus is one of the best vegetable sources of folate. Just one cup of cooked asparagus provides about 34% of the recommended daily intake. Adequate folate levels can help reduce cortisol and improve mood.
More Ways to Manage Cortisol Levels
Aside from eating the aforementioned foods, here are some ways to keep cortisol in check:
Exercise Regularly: Moderate exercise can help reduce cortisol levels, but overtraining can have the opposite effect.
Practice Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, and mindfulness can help lower cortisol.
Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support healthy cortisol rhythms.
Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can increase cortisol levels, so drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Limit Stimulants: Reduce caffeine and alcohol intake, as they can spike cortisol levels.